BNB is the native utility token of the BNB Chain ecosystem, serving as both the foundational cryptocurrency for the Binance exchange platform and the operational fuel for its blockchain infrastructure. It powers transactions, pays network fees, and enables participation in governance across the BNB Chain ecosystem.
How BNB Started and Evolved
BNB launched in July 2017 as an ERC-20 token on Ethereum. Created by Binance founder Changpeng Zhao (CZ), it was originally designed to give users a 50% discount on trading fees when paying with BNB. As Binance grew, so did BNB’s role. In 2019, Binance moved BNB to its own blockchain network called BNB Chain. This allowed BNB to handle more complex tasks beyond simple fee discounts. Today, BNB is no longer just a token-it’s the backbone of a thriving ecosystem with thousands of decentralized applications.
How BNB Works: Tokenomics and Consensus
BNB’s design includes a smart burn mechanism. The total supply started at 200 million tokens, but Binance burns 1 million BNB every quarter using fees collected from the network. By Q4 2023, over 48 million tokens had been destroyed, reducing the circulating supply to about 144 million. This process keeps BNB scarce and potentially increases its value over time. The BNB Chain uses a Proof of Stake Authority (PoSA) consensus mechanism, combining elements of Proof of Stake and Proof of Authority. This setup lets BNB Chain handle up to 100 transactions per second-much faster than Ethereum’s 15-30 TPS-and keeps transaction fees low, typically between $0.05 and $0.10 per transaction.
BNB’s Ecosystem: More Than Just a Token
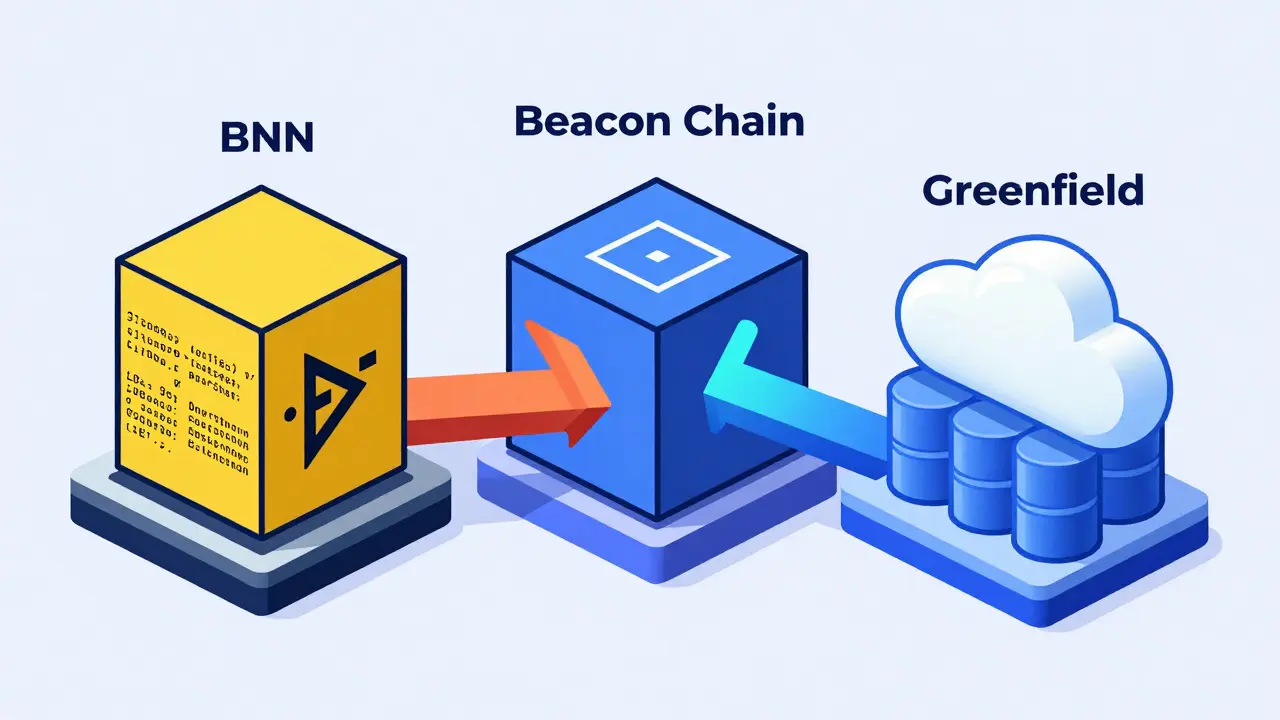
BNB Chain isn’t a single blockchain. It’s made up of three main parts:
- BNB Smart Chain handles smart contracts and decentralized apps (dApps). It’s compatible with Ethereum’s tools, so developers can build on it using Solidity.
- BNB Beacon Chain manages governance and staking. However, it’s scheduled to be retired in June 2024, with its functions moving to BNB Smart Chain.
- BNB Greenfield a decentralized storage solution launched in late 2023, allowing users to store data securely without relying on central servers.
These components support over 1,500 active projects. For example, PancakeSwap is a top decentralized exchange processing over $1 billion in daily trading volume using BNB.. Other projects include Venus Protocol for lending and various NFT platforms.

BNB in Action: Real-World Uses
People use BNB in many practical ways:
- Trading fees: On Binance, using BNB cuts trading fees by up to 25%. For active traders, this saves hundreds of dollars annually.
- DeFi: Users stake BNB on platforms like PancakeSwap to earn rewards. Some farms offer 10-35% annual returns.
- NFTs: Minting and trading NFTs on BNB Smart Chain costs far less than Ethereum. A typical NFT transaction might cost $0.10 instead of $5+ on Ethereum.
- Payments: Services like Travala.com accept BNB for hotel bookings, and Binance Pay lets merchants accept crypto payments globally.
Reddit users often share stories like "Using BNB for gas fees on BSC saved me hundreds in transaction costs, especially for small trades under $100." This highlights BNB’s real value beyond just speculation.
BNB vs. Other Cryptocurrencies
| Feature | BNB | Ethereum | Bitcoin | Solana |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | 100 TPS | 15-30 TPS | 7 TPS | 50,000+ TPS |
| Average Transaction Fee | $0.05-$0.10 | $1.50-$5.00 | $3-$10 | $0.001-$0.01 |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Stake Authority | Proof of Stake | Proof of Work | Proof of History |
| Validator Nodes | 41 | 800,000+ | 10,000+ | 1,000+ |
| Primary Use Case | Exchange utility + ecosystem fuel | Smart contracts | Digital gold | High-speed transactions |
BNB sits in a unique spot. Unlike Bitcoin, which is mainly a store of value, BNB has real utility in trading and decentralized apps. Compared to Ethereum, BNB offers similar smart contract capabilities at a fraction of the cost. Solana is faster but more centralized-BNB’s 41 validator nodes (though still centralized compared to Ethereum) balance speed and decentralization better for many users.
Pros and Cons of BNB
Pros:
- Low fees: Transaction costs on BNB Smart Chain are among the lowest in the industry.
- Strong ecosystem: Over 1,500 projects across DeFi, NFTs, and gaming rely on BNB.
- Exchange integration: Binance’s massive user base ensures constant demand for BNB.
- Burn mechanism: Regular token burns reduce supply, potentially increasing value over time.
Cons:
- Centralization risks: Binance controls many aspects of BNB Chain, including validator nodes.
- Regulatory scrutiny: Binance’s $4.3 billion settlement with U.S. regulators in 2023 created uncertainty.
- Security concerns: BNB Chain has faced 17 major security incidents in 2023, costing users $287 million.
These factors make BNB powerful but also highlight why it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. For everyday users, the benefits often outweigh the risks-but it’s important to stay informed.
Current Status and Future Roadmap
As of early 2024, BNB has a market cap of over $86 billion and ranks third among cryptocurrencies. Binance processes $55 billion in daily trading volume, with 180 million registered users globally. The "Fusion" roadmap aims to simplify the ecosystem:
- Retiring the BNB Beacon Chain in June 2024 and merging its functions into BNB Smart Chain.
- Launching "opBNB an optimized layer-2 scaling solution targeting 4,000+ transactions per second.", scheduled for mainnet launch in Q3 2024.
- Expanding BNB Greenfield storage to support 100 petabytes of data by 2025.
- Integrating Binance Pay with 1 million monthly merchant transactions by end of 2024.
Analysts like Standard Chartered predict BNB could reach $1,200 by 2026, while Bernstein cautions about regulatory hurdles. Regardless, BNB’s evolution from a simple fee discount tool to a multi-faceted blockchain ecosystem shows its staying power.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is BNB used for?
BNB serves multiple purposes: it pays for transaction fees on Binance and BNB Chain, enables participation in decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms like PancakeSwap, allows minting NFTs at low costs, and is accepted for payments through services like Travala.com and Binance Pay. Originally designed for trading fee discounts, it now powers an entire ecosystem of applications.
How does the BNB burn mechanism work?
Binance burns 1 million BNB tokens every quarter using fees collected from the network. This process started in 2017 and has destroyed over 48.4 million tokens by Q4 2023. The goal is to reduce the total supply from 200 million to 100 million, making BNB scarcer over time. This scarcity can potentially increase the token’s value as demand grows while supply decreases.
Is BNB safe to use?
BNB itself is secure, but like all cryptocurrencies, it depends on how you use it. BNB Chain has faced security incidents, including $287 million in losses in 2023 due to smart contract vulnerabilities. Users should only interact with trusted dApps, use hardware wallets for storage, and stay updated on platform security practices. Binance also provides extensive documentation and 24/7 support to help users stay safe.
Can I use BNB outside of Binance?
Yes! BNB is accepted for payments on platforms like Travala.com for travel bookings and Binance Pay for merchant transactions. It’s also widely used in DeFi apps such as PancakeSwap for trading and staking, and in NFT marketplaces like BakerySwap. Many wallets like Trust Wallet and MetaMask support BNB, making it easy to use across different services beyond Binance.
How does BNB compare to Ethereum?
BNB Smart Chain and Ethereum both support smart contracts and dApps, but BNB offers faster transactions (100 TPS vs. 15-30 TPS) and much lower fees ($0.05-$0.10 vs. $1.50-$5.00 per transaction). Ethereum has a larger developer community and more decentralized validator nodes (800,000+ vs. BNB’s 41), but BNB provides a more cost-effective option for everyday users and developers building on a budget. BNB is also more centralized, which is a trade-off for speed and affordability.

Comments
Brittany Novak
Binance's 'burn mechanism' is a complete sham. They're secretly hoarding BNB while pretending to reduce supply. The entire system is designed to manipulate prices. Trust me, this is a classic pump-and-dump scheme. They control the validator nodes and the tokenomics. It's all a facade.
February 7, 2026 at 08:41
Reda Adaou
I've been using BNB for DeFi for a while now and it's been smooth sailing. I can help with staking or PancakeSwap if needed.
February 8, 2026 at 04:08
perry jody
Wow, BNB is absolutely crushing it! 🚀 The low fees and fast transactions make it perfect for everyday use. I've saved so much on trading fees and it's awesome. Definitely give it a try! 😄
February 8, 2026 at 14:23
Robin Ødis
Okay, so I've been following crypto for like 10 years now, and let me tell you, BNB is the real deal. Binance has done a great job, but... wait, no, actually they're not perfect. The burn mechanism is cool but... I don't know. Maybe they should do more. Anyway, I think people should be careful. I've seen too many scams. But BNB is legit. I think so. Maybe. I don't know. Also, the security issues are concerning. They lost millions last year. But Binance is trying to fix it. I guess. Not sure. Maybe check the official docs. Wait, I forgot to mention that the validator nodes are controlled by Binance, which is a problem. Also, the tokenomics are confusing. They say they burn tokens but it's unclear how much is actually burned. Plus, the market cap is inflated because of Binance's influence. And the fact that they have to deal with regulatory issues. The SEC is probably going to come after them. So overall, I'm not sure if BNB is safe. Maybe it's better to stick with Bitcoin. But I don't know. Maybe I'm wrong. I'm just saying, be careful.
February 10, 2026 at 07:23
Jacque Istok
Oh sure, BNB's low fees are great. But let's not ignore the 17 security incidents last year. $287 million lost. Great job, Binance. 🤦♀️
February 11, 2026 at 19:25
laura mundy
BNB is a scam.
February 13, 2026 at 11:35
David Bain
BNB's Proof of Stake Authority consensus mechanism represents a bifurcation of trust models within the blockchain ecosystem. The 41 validator nodes exemplify a centralized governance structure which, while efficient for transaction throughput, fundamentally undermines the decentralized ethos that underpins cryptographic systems. This structural contradiction necessitates critical evaluation of BNB's long-term viability.
February 14, 2026 at 16:02
Michael Sullivan
BNB is a dumpster fire. 🗑️🔥 17 hacks in a year. $287M lost. Binance's 'burn' is just PR. Don't touch it.
February 14, 2026 at 16:57
Olivette Petersen
BNB's ecosystem is thriving! So many projects building on it. I'm excited to see how it evolves. Keep pushing forward! 💪
February 16, 2026 at 16:24